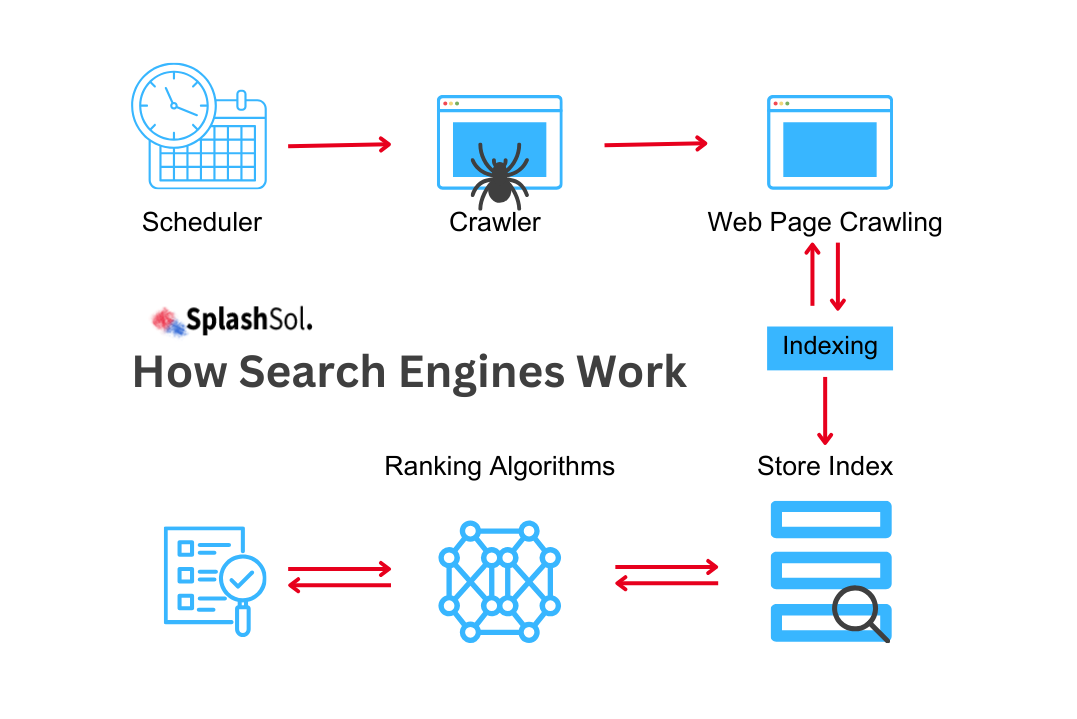
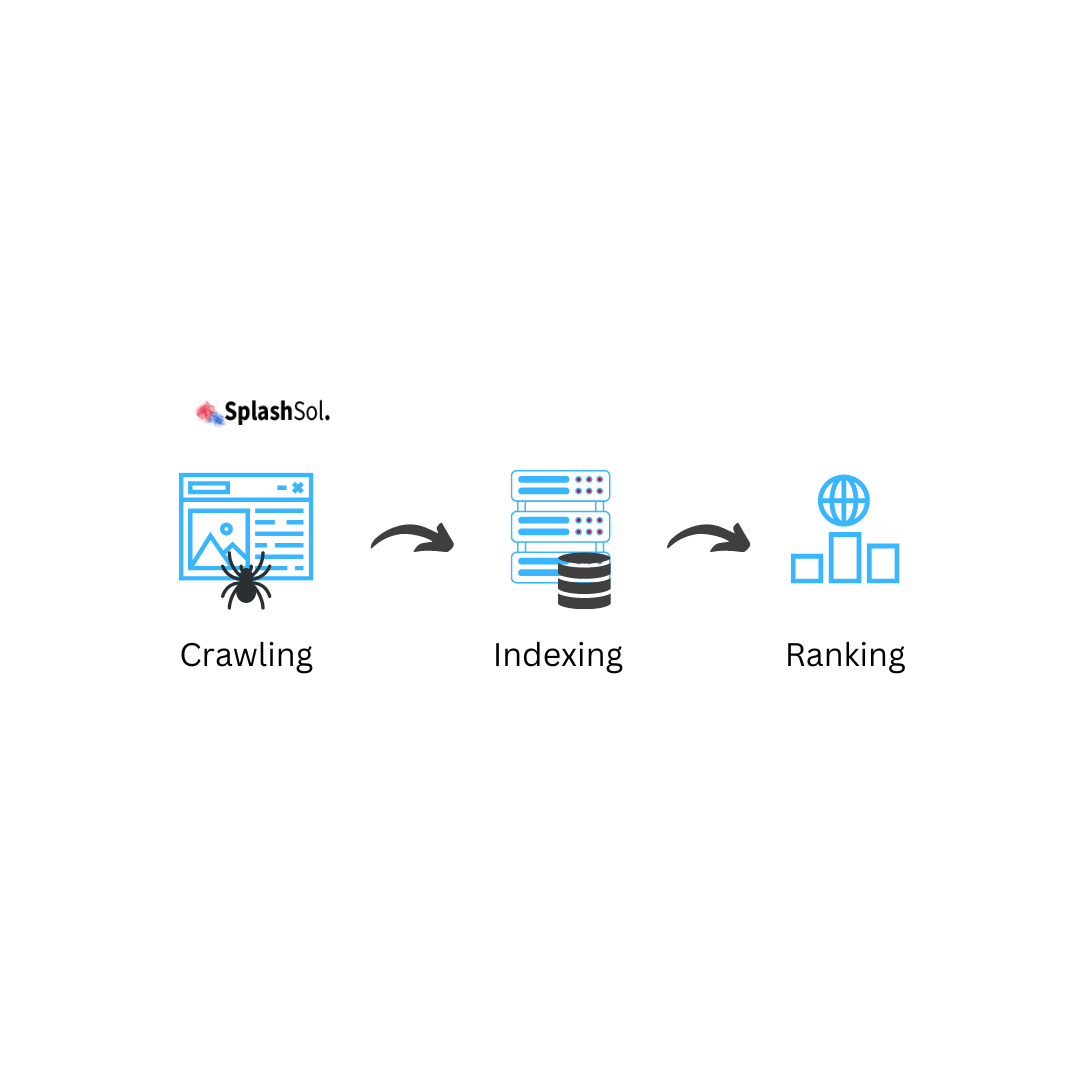
In this expanding digital landscape, the sheer volume of web content continues to grow rapidly. With billions of web pages and a seemingly infinite amount of data to crawl and index, search engines like Google face a monumental task.
This blog post discusses the complexities of Google’s crawling and indexing processes, and we will also learn how the search giant handles the vast expanse of information on the internet.
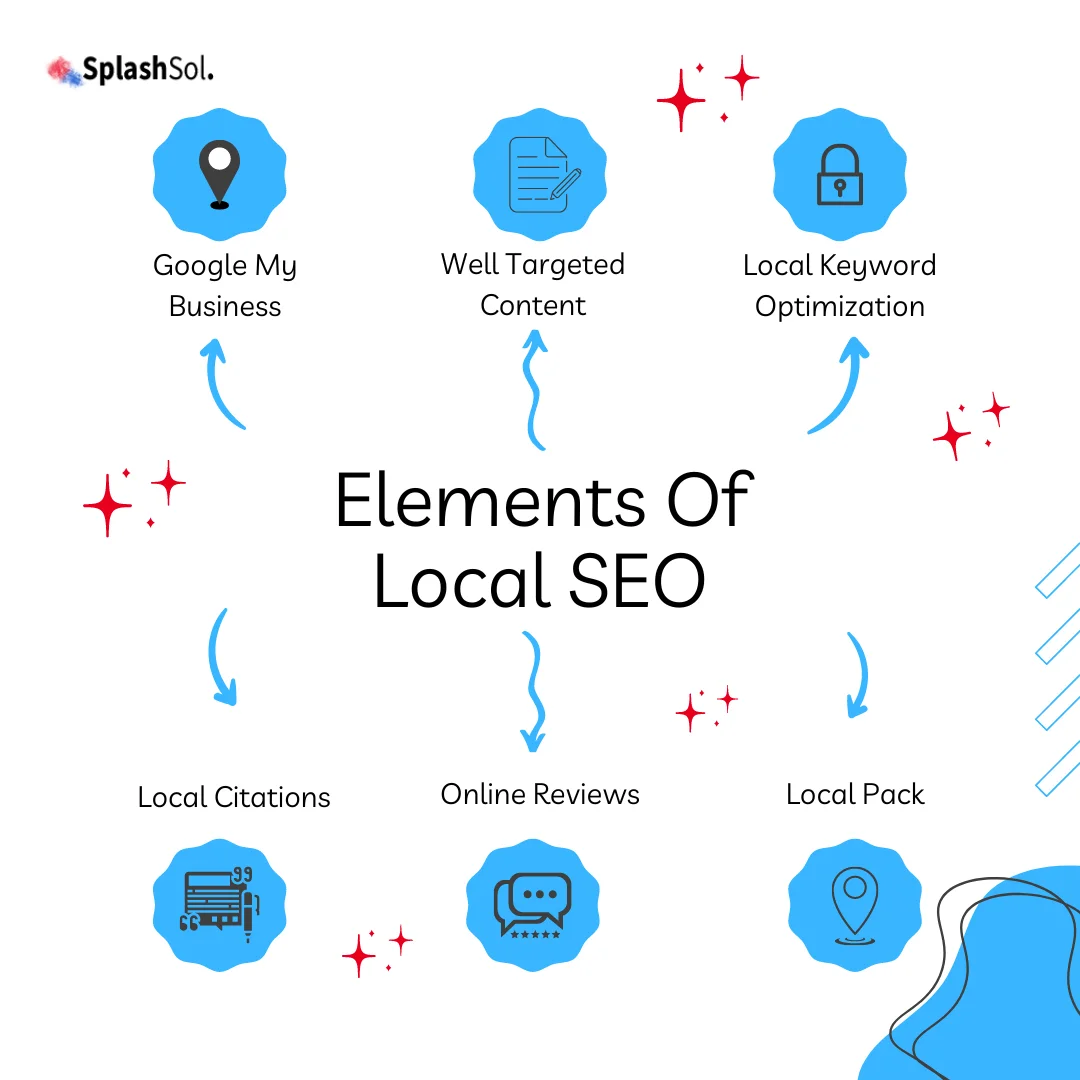
The Crawl Rate Vs Indexing Rate
Before we further discuss Google’s web management, it’s essential to understand the distinction between crawl and indexing rates. This is a fundamental concept in understanding the complexities of how Google operates.
| Crawl Rate |
Indexing Rate |
| The crawl rate defines the speed at which Googlebot explores and requests web pages. It serves as the heartbeat of the crawling process, determining how swiftly Google can traverse the web. |
The indexing rate represents the pace at which pages are added to Google’s index, making them searchable in search results. Not all crawled pages make it to the index because of Google’s rigorous quality filter. |
The Importance Of Quality Pages
The web is not just flooded with billions of quality pages that suddenly appear out of nowhere. The key emphasis here is on “quality” pages.
Google’s algorithms are designed to prioritise high-quality content and disregard low-quality or spammy pages. Therefore, not all pages on the internet are of interest to Google, and the search engine must be discerning in its crawling and indexing processes.
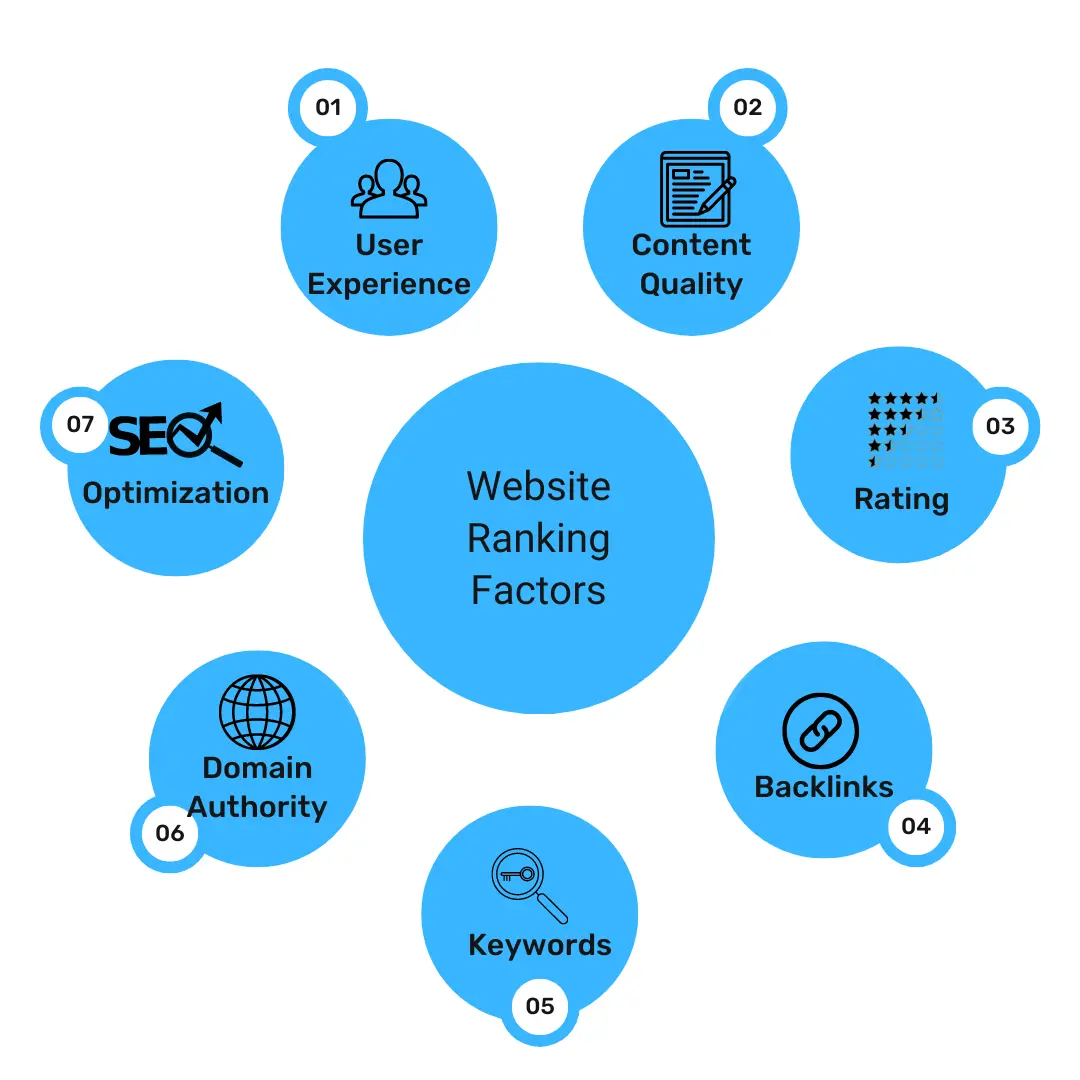
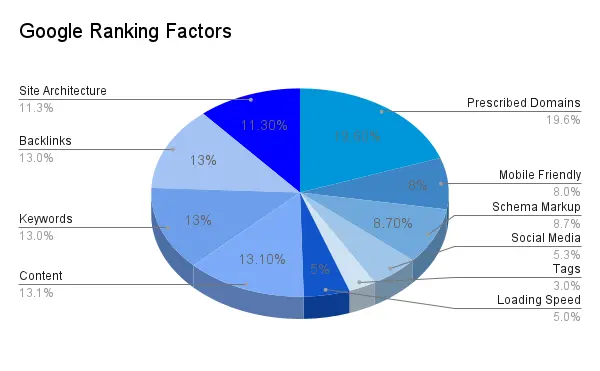
Google’s ability to identify quality pages is based on a combination of factors, including:
| Page Rank |
The PageRank algorithm, developed by Google’s co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin, evaluates the importance of web pages based on the number and quality of links pointing to them. Pages with higher PageRank are considered more authoritative and are more likely to be crawled and indexed. |
| Content Quality |
Google assesses the quality of content on web pages. Pages with well-researched, informative, and engaging content are more likely to be crawled and indexed. |
| User Experience |
Google takes into account the user experience, including factors like page loading speed, mobile-friendliness, and the absence of intrusive ads. Pages that offer a better user experience are favoured. |
Crawl Modes
Googlebot does not operate in a single mode; it possesses various crawl modes, each tailored to specific aspects of the indexing process. Let us take a closer look at these modes:
Re-Crawl Mode
In this mode, Googlebot frequently revisits and re-crawls pages that have already been indexed, searching for updates or changes. This ensures that search results stay fresh and up-to-date.
Fresh Crawl Mode
Websites with high PageRank or frequently changing content trigger this mode. Googlebot extensively crawls new and updated pages to capture the most recent information.
Stale Pages Mode
In this mode, Googlebot explores older links or pages that may no longer exist. These pages often hold historical significance and typically have low PageRank. They are crawled in URL-length order.
Strategies To Optimise For Faster Crawling
If you are looking to improve your website’s crawl rate, consider the following strategies:
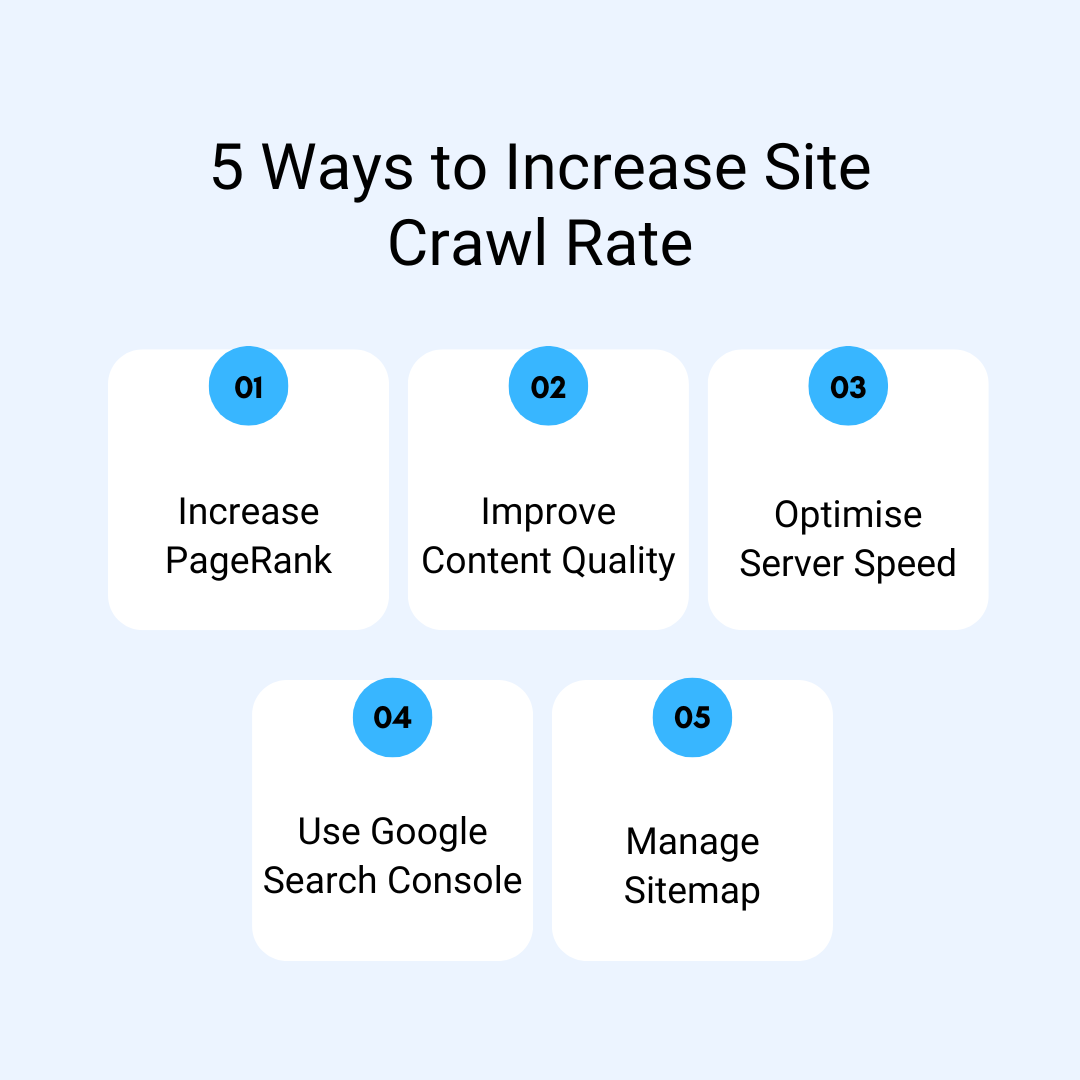
Increase PageRank
Build high-quality backlinks to your website to enhance its PageRank, which can lead to more frequent and deeper crawls.
Improve Content Quality
Ensure that your website offers valuable and unique content that appeals to both users and ensures better search engine optimisation.
Optimise Server Speed
Enhance your server’s response time to accommodate faster crawling. This may involve optimising your code, database, and server infrastructure.
Utilise Google Search Console
Adjust your crawl rate settings in Google Search Console to influence how frequently Googlebot crawls your site.
Sitemap Management
Use dynamic sitemaps effectively, and consider adding sub-sitemaps to Google Search Console and your robots.txt file to facilitate crawling.
Mobile-First Indexing And Its Impact
In recent years, Google has made a fundamental shift in its indexing process. Mobile-first indexing has taken centre stage.
This approach means that Google predominantly uses the mobile version of a website for ranking and indexing, considering the growing importance of mobile browsing. This shift has significant implications for website owners and SEO practitioners.
With Mobile-First Indexing, the mobile version of your site becomes the starting point for how Google determines rankings. So, making your digital marketing strategy to ensure that your website is not only mobile-friendly but offers a stellar mobile experience is paramount.
Factors like responsive design, fast mobile page load times, and the usability of your mobile site play a crucial role in this context.
Structured Data And Rich Snippets
Structured data, often called schema markup, is a powerful tool that webmasters can use to provide search engines with additional information about the content on their web pages. When used effectively, structured data can result in the display of rich snippets in search results.
Rich snippets are search results that include additional information, such as star ratings, product prices, event dates, and more.
Here’s why structured data and rich snippets are essential in the context of Google’s web management:
| Improved Visibility |
Web pages with rich snippets stand out in search results. They provide users with a preview of what to expect, making your content more enticing. |
| Enhanced Click-Through Rates |
Rich snippets can lead to higher click-through rates (CTR) because users are more likely to click on visually appealing and informative results. |
| Structured Content |
Search engines use structured data to understand the content and context of a web page better. This can lead to improved rankings for relevant queries. |
| Different Types Of Structured Data |
There are various types of structured data for different types of content, including products, events, recipes, and more. By implementing the appropriate structured data for your content, you can take advantage of rich snippets in relevant search queries. |
To implement structured data on your website, you can use schema markup or JSON-LD to provide search engines with structured information about your pages.
Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool can help you validate and test your structured data implementation to ensure it’s error-free and ready for indexing.
A Cautionary Note On Crawl Speed
While pushing for the fastest crawl rate possible is tempting, ensuring that your server can handle it is essential.
Setting a crawl rate that exceeds your server’s capacity may result in numerous 4xx and 5xx HTTP status responses, which can negatively impact your website’s relationship with Google.
These errors can lead to a decreased crawl budget and slower indexing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the crawl rate in Google’s indexing process?
The crawl rate determines how quickly Googlebot explores and requests pages from websites. It influences the speed at which a website’s content is examined for potential inclusion in search results. A higher crawl rate can lead to more pages being indexed.
What is the difference between the crawl rate and indexing rate?
The crawl rate is the speed at which Google explores web pages, while the indexing rate is the pace at which pages are added to Google’s index, making them searchable. Not all crawled pages are indexed, as Google applies quality filters.
How can I improve my website’s crawl rate?
To enhance your website’s crawl rate, consider strategies like improving PageRank through quality backlinks, optimising server responsiveness, and using Google Search Console to customise crawl rate settings.
What is the role of content quality in Google’s selective crawling?
Content quality, including relevance, trustworthiness, and user experience, plays a pivotal role in Google’s selective crawling. Pages with high-quality content are more likely to be crawled and indexed.
Why is it essential to exercise caution when increasing crawl speed?
Boosting crawl speed beyond a server’s capacity can result in an excess of 4xx and 5xx HTTP status responses, which can harm your website’s relationship with Google. It may lead to a reduced crawl budget and slower indexing.